 DE
DE


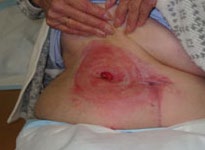
Case study submitted by: Margie Reid, Clinical Practice Consultant, Stomal Therapy Nurse (Credentialled), Adelaide, South Australia.




Superior absorption4
High protection against enzymes 3,4
Combats irritants3,4
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website, anonymously.
| Cookie | Dauer | Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|
| __cfduid | 1 month | The cookie is used by cdn services like CloudFare to identify individual clients behind a shared IP address and apply security settings on a per-client basis. It does not correspond to any user ID in the web application and does not store any personally identifiable information. |
| _wpfuuid | 11 years | This cookie is used by the WPForms WordPress plugin. The cookie is used to allows the paid version of the plugin to connect entries by the same user and is used for some additional features like the Form Abandonment addon. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-advertisement | 1 year | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Advertisement". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 1 year | This cookies is set by GDPR Cookie Consent WordPress Plugin. The cookie is used to remember the user consent for the cookies under the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 1 year | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 1 year | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| icwp-app-flash | past | Cookie generated by our website management tool, iControlWP. icwp-app-flash is used to store a temporary wp admin message |
| icwp-wpsf-notbot | 10 minutes | This cookie is placed by WordPress to detect bots. |
| pouch_page_journey | session | This cookie enables us to remember your selections as you search our ostomy pouches based on ostomy type. |
Performance cookies are used to understand and analyze the key performance indexes of the website which helps in delivering a better user experience for the visitors.
| Cookie | Dauer | Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|
| _wpfuuid | 11 years | This cookie is used by the WPForms WordPress plugin. The cookie is used to allows the paid version of the plugin to connect entries by the same user and is used for some additional features like the Form Abandonment addon. |
| test_cookie | 15 minutes | This cookie is set by doubleclick.net. The purpose of the cookie is to determine if the user's browser supports cookies. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 1 year | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
| wordpress_country | 2 months | This cookie allows us to remember which country you selected so that we only show products that are available in your country. |
| wordpress_survery_timer | 7 days | This cookie is used when we place a user feedback on the site so that it only shows up after a specified amount of time. |
| YSC | session | This cookies is set by Youtube and is used to track the views of embedded videos. |
Advertisement cookies are used to provide visitors with relevant ads and marketing campaigns. These cookies track visitors across websites and collect information to provide customized ads.
| Cookie | Dauer | Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|
| _fbp | We use Facebook ads from time to time to help direct users to pages of interest on our website. Facebook may use cookies or web beacons to collect or receive information from our website. We use that information to compile reports and help us target our advertising more effectively. | |
| fr | 3 months | The cookie is set by Facebook to show relevant advertisments to the users and measure and improve the advertisements. The cookie also tracks the behavior of the user across the web on sites that have Facebook pixel or Facebook social plugin. |
| IDE | 1 year 24 days | Used by Google DoubleClick and stores information about how the user uses the website and any other advertisement before visiting the website. This is used to present users with ads that are relevant to them according to the user profile. |
| RUL | 1 year | Used by DoubleClick to determine whether website advertisement has been properly displayed - This is done to make their marketing efforts more efficient. |
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information on metrics the number of visitors, bounce rate, traffic source, etc.
| Cookie | Dauer | Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|
| _ga | 2 years | This cookie is installed by Google Analytics. The cookie is used to calculate visitor, session, campaign data and keep track of site usage for the site's analytics report. The cookies store information anonymously and assign a randomly generated number to identify unique visitors. |
| _gat_gtag_UA_143265736_1 | 1 minute | This cookie is used by Google Analytics to help us analyse traffic to our site. |
| _gid | 1 day | This cookie is installed by Google Analytics. The cookie is used to store information of how visitors use a website and helps in creating an analytics report of how the wbsite is doing. The data collected including the number visitors, the source where they have come from, and the pages viisted in an anonymous form. |
| VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE | 5 months 27 days | This cookie is set by Youtube. Used to track the information of the embedded YouTube videos on a website. |
| vuid | 2 years | This domain of this cookie is owned by Vimeo. This cookie is used by vimeo to collect tracking information. It sets a unique ID to embed videos to the website. |